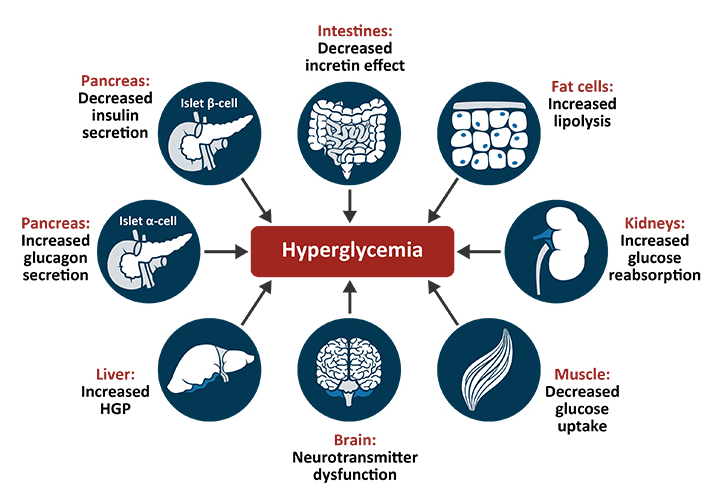
Prevention
There is no known preventive measure for type 1 diabetes. However, islet autoimmunity and multiple antibodies can be a strong predictor of the onset of type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes—which accounts for 85–90% of all cases worldwide —can often be prevented or delayed by maintaining a normal body weight, engaging in physical activity, and eating a healthy diet. Higher levels of physical activity (more than 90 minutes per day) reduce the risk of diabetes by 28%. Dietary changes known to be effective in helping to prevent diabetes include maintaining a diet rich in whole grains and fiber, and choosing good fats, such as the polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, vegetable oils, and fish. Limiting sugary beverages and eating less red meat and other sources of saturated fat can also help prevent diabetes. Tobacco smoking is also associated with an increased risk of diabetes and its complications, so smoking cessation can be an important preventive measure as well.
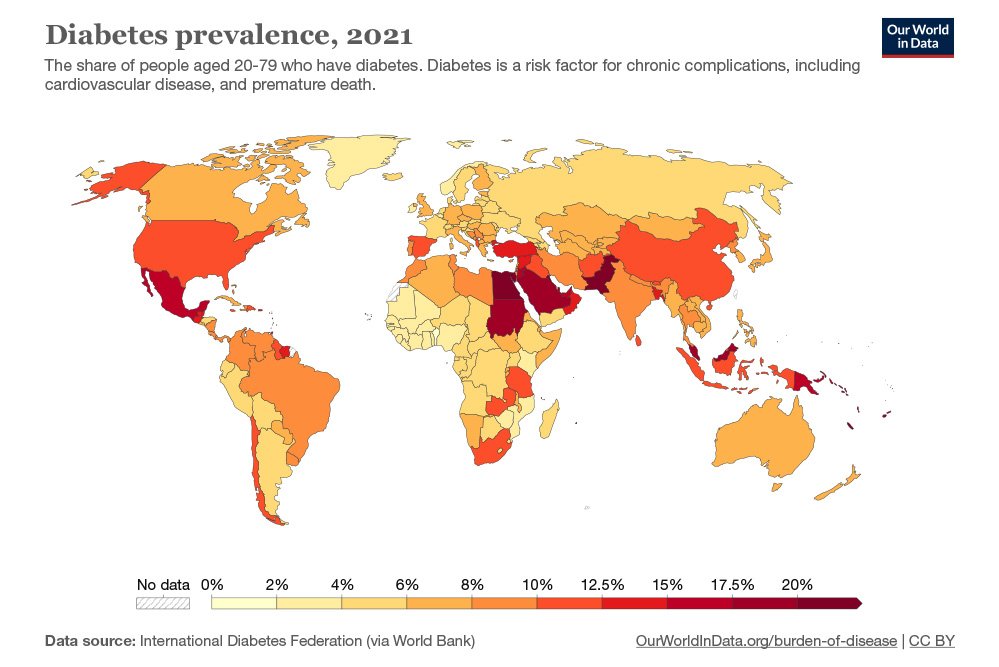
The relationship between type 2 diabetes and the main modifiable risk factors (excess weight, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and tobacco use) is similar in all regions of the world. There is growing evidence that the underlying determinants of diabetes are a reflection of the major forces driving social, economic and cultural change: globalization, urbanization, population aging, and the general health policy environment.