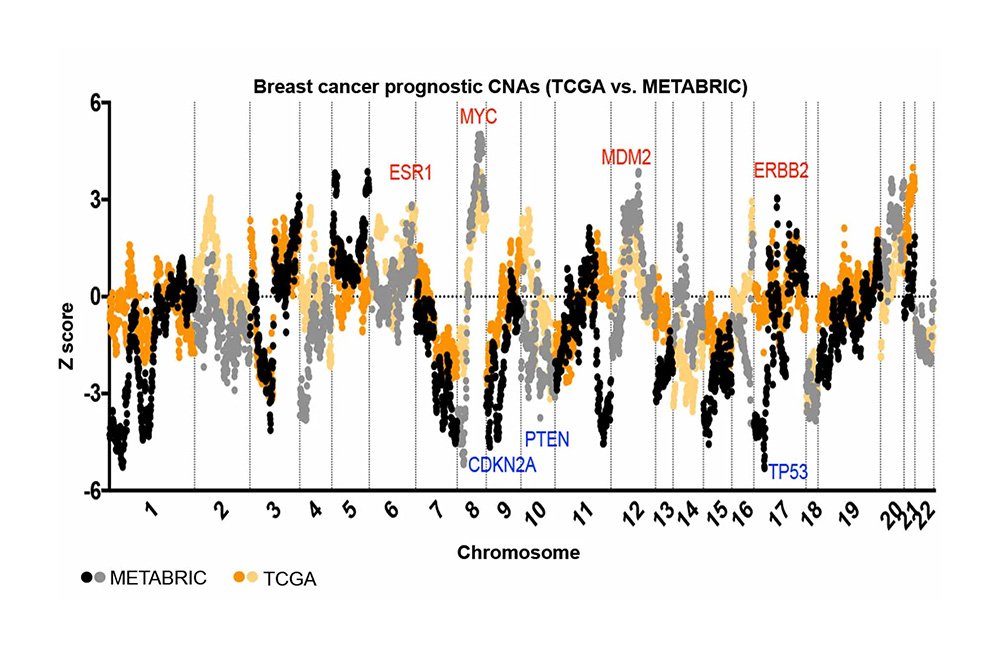
Etymology and Definitions
Cancers comprise a large family of diseases that involve abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. They form a subset of neoplasms. A neoplasm or tumor is a group of cells that have undergone unregulated growth and will often form a mass or lump, but may be distributed diffusely.
All tumor cells show the six hallmarks of cancer. These characteristics are required to produce a malignant tumor. They include:
- Cell growth and division absent the proper signals
- Continuous growth and division even given contrary signals
- Avoidance of programmed cell death
- Limitless number of cell divisions
- Promoting blood vessel construction
- Invasion of tissue and formation of metastasis
The progression from normal cells to cells that can form a detectable mass to cancer involves multiple steps known as malignant progression.

A coronal CT scan showing a malignant mesothelioma
Legend: → tumor ←, ✱ central pleural effusion, 1 & 3 lungs, 2 spine, 4 ribs, 5 aorta, 6 spleen, 7 & 8 kidneys, 9 liver