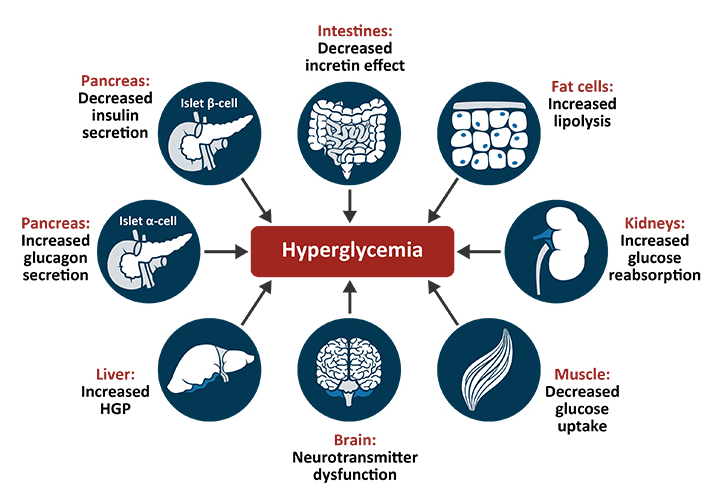
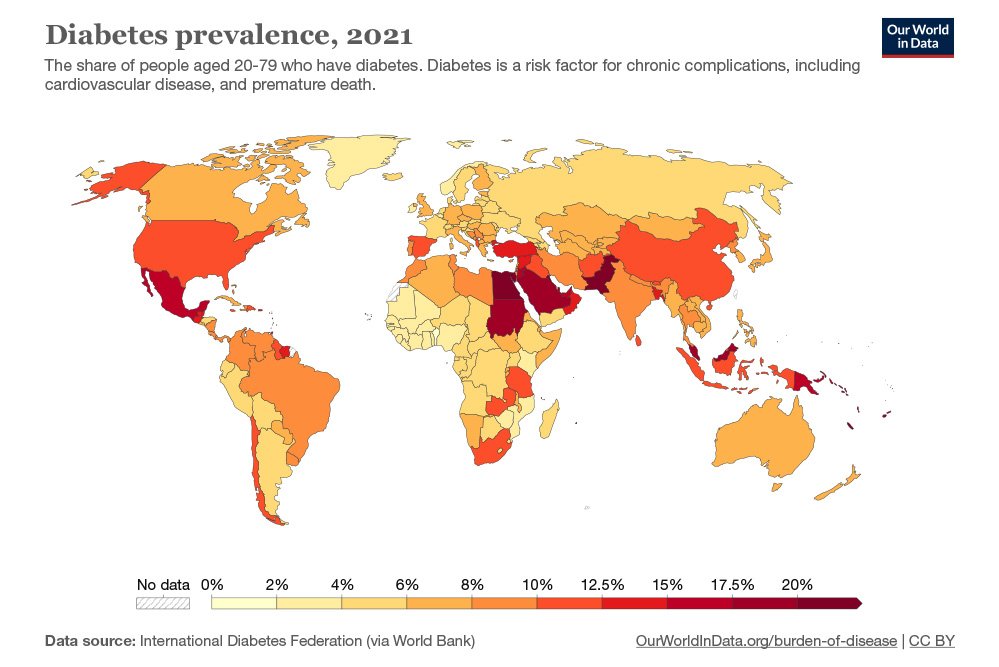
History of Diabetes
Diabetes was one of the first diseases described, with an Egyptian manuscript from c. 1500 BCE mentioning “too great emptying of the urine.” The Ebers papyrus includes a recommendation for a drink to take in such cases. The first described cases are believed to have been type 1 diabetes. Indian physicians around the same time identified the disease and classified it as madhumeha or “honey urine”, noting the urine would attract ants.
The term “diabetes” or “to pass through” was first used in 230 BCE by the Greek Apollonius of Memphis. The disease was considered rare during the time of the Roman empire, with Galen commenting he had only seen two cases during his career. This is possibly due to the diet and lifestyle of the ancients, or because the clinical symptoms were observed during the advanced stage of the disease. Galen named the disease “diarrhea of the urine” (diarrhea urinosa).
The earliest surviving work with a detailed reference to diabetes is that of Aretaeus of Cappadocia (2nd or early 3rd century CE). He described the symptoms and the course of the disease, which he attributed to the moisture and coldness, reflecting the beliefs of the “Pneumatic School”. He hypothesized a correlation between diabetes and other diseases, and he discussed differential diagnosis from the snakebite, which also provokes excessive thirst. His work remained unknown in the West until 1552, when the first Latin ion was published in Venice.
Two types of diabetes were identified as separate conditions for the first time by the Indian physicians Sushruta and Charaka in 400–500 CE with one type being associated with youth and another type with being overweight. Effective treatment was not developed until the early part of the 20th century when Canadians Frederick Banting and Charles Best isolated and purified insulin in 1921 and 1922. This was followed by the development of the long-acting insulin NPH in the 1940s.
Etymology
The word diabetes (/ˌdaɪ.əˈbiːtiːz/ or /ˌdaɪ.əˈbiːtɪs/) comes from Latin diabētēs, which in turn comes from Ancient Greek διαβήτης (diabētēs), which literally means “a passer through; a siphon”. Ancient Greek physician Aretaeus of Cappadocia (fl. 1st century CE) used that word, with the intended meaning “excessive discharge of urine”, as the name for the disease. Ultimately, the word comes from Greek διαβαί
νειν (diabainein), meaning “to pass through”, which is composed of δια- (dia-), meaning “through” and βαίνειν (bainein), meaning “to go”. The word “diabetes” is first recorded in English, in the form diabete, in a medical text written around 1425.
The word mellitus (/məˈlaɪtəs/ or /ˈmɛlɪtəs/) comes from the classical Latin word mellītus, meaning “mellite” (i.e. sweetened with honey; honey-sweet). The Latin word comes from mell-, which comes from mel, meaning “honey”; sweetness; pleasant thing, and the suffix -ītus, whose meaning is the same as that of the English suffix “-ite”. It was Thomas Willis who in 1675 added “mellitus” to the word “diabetes” as a designation for the disease, when he noticed the urine of a person with diabetes had a sweet taste (glycosuria). This sweet taste had been noticed in urine by the ancient Greeks, Chinese, Egyptians, Indians, and Persians.