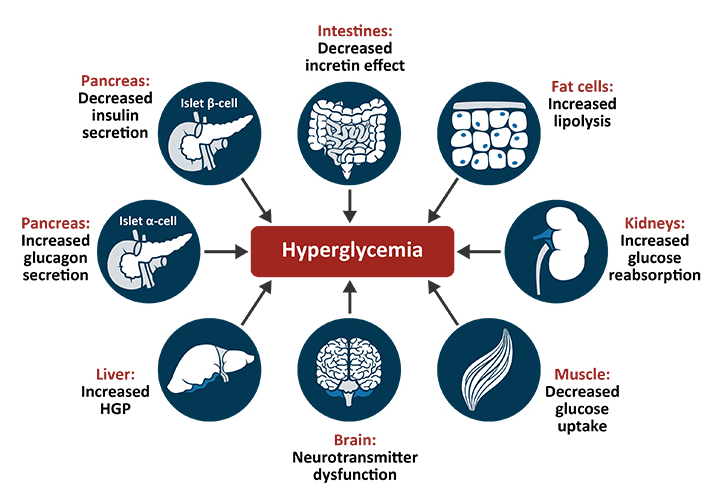
Causes of Diabetes
Diabetes is classified by the World Health Organization into six categories: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, hybrid forms of diabetes (including slowly evolving, immune-mediated diabetes of adults and ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes), hyperglycemia first detected during pregnancy, “other specific types”, and “unclassified diabetes”. Diabetes is a more variable disease than once thought, and individuals may have a combination of forms.
| Feature | Type 1 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Age at onset | Any age; average age at diagnosis being 24 | Mostly in adults |
| Body size | Thin or normal | Often |
| Ketoacidosis | Common | Rare |
| Autoantibodies | Usually present | Absent |
| Endogenous insulin | Low or absent | Normal, decreased or increased |
| Heritability | 0.69 to 0.88 | 0.47 to 0.77 |
| Prevalence (age standardized) | <2 per 1,000 | ~6% (men), ~5% (women) |
Type 1
Type 1 accounts for 5 to 10% of diabetes cases and is the most common type diagnosed in patients under 20 years; however, the older term “juvenile-onset diabetes” is no longer used as the disease not uncommonly has onset in adulthood. The disease is characterized by loss of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreatic islets, leading to severe insulin deficiency, and can be further classified as immune-mediated or idiopathic (without known cause). The majority of cases are immune-mediated, in which a T cell-mediated autoimmune attack causes loss of beta cells and thus insulin deficiency. Patients often have irregular and unpredictable blood sugar levels due to very low insulin and an impaired counter-response to hypoglycaemia.
Type 1 diabetes is partly inherited, with multiple genes, including certain HLA genotypes, known to influence the risk of diabetes. In genetically susceptible people, the onset of diabetes can be triggered by one or more environmental factors, such as a viral infection or diet. Several viruses have been implicated, but to date there is no stringent evidence to support this hypothesis in humans.
Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, and a significant proportion is diagnosed during adulthood. Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA) is the diagnostic term applied when type 1 diabetes develops in adults; it has a slower onset than the same condition in children. Given this difference, some use the unofficial term “type 1.5 diabetes” for this condition. Adults with LADA are frequently initially misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes, based on age rather than a cause. LADA leaves adults with higher levels of insulin production than type 1 diabetes, but not enough insulin production for healthy blood sugar levels.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, which may be combined with relatively reduced insulin secretion. The defective responsiveness of body tissues to insulin is believed to involve the insulin receptor. However, the specific defects are not known. Diabetes mellitus cases due to a known defect are classified separately. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes mellitus accounting for 95% of diabetes. Many people with type 2 diabetes have evidence of prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) before meeting the criteria for type 2 diabetes. The progression of prediabetes to overt type 2 diabetes can be slowed or reversed by lifestyle changes or medications that improve insulin sensitivity or reduce the liver’s glucose production.
Type 2 diabetes is primarily due to lifestyle factors and genetics. A number of lifestyle factors are known to be important to the development of type 2 diabetes, including obesity (defined by a body mass index of greater than 30), lack of physical activity, poor diet, stress, and urbanization. Excess body fat is associated with 30% of cases in people of Chinese and Japanese descent, 60–80% of cases in those of European and African descent, and 100% of Pima Indians and Pacific Islanders. Even those who are not obese may have a high waist–hip ratio.
Dietary factors such as sugar-sweetened drinks are associated with an increased risk. The type of fats in the diet is also important, with saturated fat and trans fats increasing the risk and polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat decreasing the risk. Eating white rice excessively may increase the risk of diabetes, especially in Chinese and Japanese people. Lack of physical activity may increase the risk of diabetes in some people.
Adverse childhood experiences, including abuse, neglect, and household difficulties, increase the likelihood of type 2 diabetes later in life by 32%, with neglect having the strongest effect.
Antipsychotic medication side effects (specifically metabolic abnormalities, dyslipidemia and weight gain) and unhealthy lifestyles (including poor diet and decreased physical activity), are potential risk factors.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes resembles type 2 diabetes in several respects, involving a combination of relatively inadequate insulin secretion and responsiveness. It occurs in about 2–10% of all pregnancies and may improve or disappear after delivery. It is recommended that all pregnant women get tested starting around 24–28 weeks gestation. It is most often diagnosed in the second or third trimester because of the increase in insulin-antagonist hormone levels that occurs at this time. However, after pregnancy approximately 5–10% of women with gestational diabetes are found to have another form of diabetes, most commonly type 2. Gestational diabetes is fully treatable, but requires careful medical supervision throughout the pregnancy. Management may include dietary changes, blood glucose monitoring, and in some cases, insulin may be required.
Though it may be transient, untreated gestational diabetes can damage the health of the fetus or mother. Risks to the baby include macrosomia (high birth weight), congenital heart and central nervous system abnormalities, and skeletal muscle malformations. Increased levels of insulin in a fetus’s blood may inhibit fetal surfactant production and cause infant respiratory distress syndrome. A high blood bilirubin level may result from red blood cell destruction. In severe cases, perinatal death may occur, most commonly as a result of poor placental perfusion due to vascular impairment. Labor induction may be indicated with decreased placental function. A caesarean section may be performed if there is marked fetal distress or an increased risk of injury associated with macrosomia, such as shoulder dystocia.
Other Types
Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a rare autosomal dominant inherited form of diabetes, due to one of several single-gene mutations causing defects in insulin production. It is significantly less common than the three main types, constituting 1–2% of all cases. The name of this disease refers to early hypotheses as to its nature. Being due to a defective gene, this disease varies in age at presentation and in severity according to the specific gene defect; thus, there are at least 13 subtypes of MODY. People with MODY often can control it without using insulin.
Some cases of diabetes are caused by the body’s tissue receptors not responding to insulin (even when insulin levels are normal, which is what separates it from type 2 diabetes); this form is very uncommon. Genetic mutations (autosomal or mitochondrial) can lead to defects in beta cell function. Abnormal insulin action may also have been genetically determined in some cases. Any disease that causes extensive damage to the pancreas may lead to diabetes (for example, chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis). Diseases associated with excessive secretion of insulin-antagonistic hormones can cause diabetes (which is typically resolved once the hormone excess is removed). Many drugs impair insulin secretion and some toxins damage pancreatic beta cells, whereas others increase insulin resistance (especially glucocorticoids which can provoke “steroid diabetes”). The ICD-10 (1992) diagnostic entity, malnutrition-related diabetes mellitus (ICD-10 code E12), was deprecated by the World Health Organization (WHO) when the current taxonomy was introduced in 1999. Yet another form of diabetes that people may develop is double diabetes. This is when a type 1 diabetic becomes insulin resistant, the hallmark for type 2 diabetes or has a family history for type 2 diabetes. It was first discovered in 1990 or 1991.
The following is a list of disorders that may increase the risk of diabetes:
Genetic defects of β-cell function
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young
- Mitochondrial DNA mutations
Genetic defects in insulin processing or insulin action
- Defects in proinsulin conversion
- Insulin gene mutations
- Insulin receptor mutations
Exocrine pancreatic defects (see Type 3c diabetes, i.e. ancreatogenic diabetes)
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Pancreatectomy
- Pancreatic neoplasia
- Cystic fibrosis
- Hemochromatosis
- Fibrocalculous pancreatopathy
Endocrinopathies
- Growth hormone excess (acromegaly)
- Cushing syndrome
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Pheochromocytoma
- Glucagonoma
Infections
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- Coxsackievirus B
Drugs
- Glucocorticoids
- Thyroid hormone
- β-adrenergic agonists
- Statins